- Difference Between 4th And 5th Generation Computer Name
- Characteristics Of 4th And 5th Generation Computers
- The Apple II Computer attracted business to utilizing computers more because it could run software programs like VisiCalc. In 1981, IBM releases a personal computer. It becomes a top seller and still sells today. It is a Windows based PC. Fifth generation computers are in developmental stage which is based on theartificial.
- Here’s a complete rundown of all the differences between each KICKR generation so you can tell them apart visually and understand the evolution of this smart trainer. Identifying Your KICKR Generation. Each KICKR has a few unique characteristics which make it easy to identify visually.
Computers are such an integral part of our everyday life now most people take them and what they have added to life totally for granted.
The difference between a fourth generation of computer and a fifth generation of computer can be the size. It can also be a new operating system, new storage capacity, or just a new look. Computer Science Secondary School +5 pts. Answered Difference between the 4th and 5th generation of the computers 2 See answers Answers.
Even more so the generation who have grown from infancy within the global desktop and laptop revolution since the 1980s.
The history of the computer goes back several decades however and there are five definable generations of computers.
Each generation is defined by a significant technological development that changes fundamentally how computers operate – leading to more compact, less expensive, but more powerful, efficient and robust machines.
1940 – 1956: First Generation – Vacuum Tubes
These early computers used vacuum tubes as circuitry and magnetic drums for memory. As a result they were enormous, literally taking up entire rooms and costing a fortune to run. These were inefficient materials which generated a lot of heat, sucked huge electricity and subsequently generated a lot of heat which caused ongoing breakdowns.
These first generation computers relied on ‘machine language’ (which is the most basic programming language that can be understood by computers). These computers were limited to solving one problem at a time. Input was based on punched cards and paper tape. Output came out on print-outs. The two notable machines of this era were the UNIVAC and ENIAC machines – the UNIVAC is the first every commercial computer which was purchased in 1951 by a business – the US Census Bureau.
1956 – 1963: Second Generation – Transistors
The replacement of vacuum tubes by transistors saw the advent of the second generation of computing. Although first invented in 1947, transistors weren’t used significantly in computers until the end of the 1950s. They were a big improvement over the vacuum tube, despite still subjecting computers to damaging levels of heat. However they were hugely superior to the vacuum tubes, making computers smaller, faster, cheaper and less heavy on electricity use. They still relied on punched card for input/printouts.
The language evolved from cryptic binary language to symbolic (‘assembly’) languages. This meant programmers could create instructions in words. About the same time high level programming languages were being developed (early versions of COBOL and FORTRAN). Transistor-driven machines were the first computers to store instructions into their memories – moving from magnetic drum to magnetic core ‘technology’. The early versions of these machines were developed for the atomic energy industry.
1964 – 1971: Third Generation – Integrated Circuits
By this phase, transistors were now being miniaturised and put on silicon chips (called semiconductors). This led to a massive increase in speed and efficiency of these machines. These were the first computers where users interacted using keyboards and monitors which interfaced with an operating system, a significant leap up from the punch cards and printouts. This enabled these machines to run several applications at once using a central program which functioned to monitor memory.
As a result of these advances which again made machines cheaper and smaller, a new mass market of users emerged during the ‘60s.
1972 – 2010: Fourth Generation – Microprocessors
This revolution can be summed in one word: Intel. The chip-maker developed the Intel 4004 chip in 1971, which positioned all computer components (CPU, memory, input/output controls) onto a single chip. What filled a room in the 1940s now fit in the palm of the hand. The Intel chip housed thousands of integrated circuits. The year 1981 saw the first ever computer (IBM) specifically designed for home use and 1984 saw the MacIntosh introduced by Apple. Microprocessors even moved beyond the realm of computers and into an increasing number of everyday products.
The increased power of these small computers meant they could be linked, creating networks. Which ultimately led to the development, birth and rapid evolution of the Internet. Other major advances during this period have been the Graphical user interface (GUI), the mouse and more recently the astounding advances in lap-top capability and hand-held devices.
2010- : Fifth Generation – Artificial Intelligence
Computer devices with artificial intelligence are still in development, but some of these technologies are beginning to emerge and be used such as voice recognition.
AI is a reality made possible by using parallel processing and superconductors. Leaning to the future, computers will be radically transformed again by quantum computation, molecular and nano technology.
The essence of fifth generation will be using these technologies to ultimately create machines which can process and respond to natural language, and have capability to learn and organise themselves.
• David Burns is Marketing and Communications Manager for Origin IT | davidb@originit.co.nz | www.originit.co.nz
Difference Between 4th And 5th Generation Computer Name
Today, it is widely recognized computer is really essential for the entire world. During the 21th century, many people were realize using computer could help them successful a lot of things with easier, either that’s for calculation or management. So, as we know computer is a very useful digital machine, but not everyone actually know how it created by. Therefore in this assignment, we would discuss all the things about computer architecture.
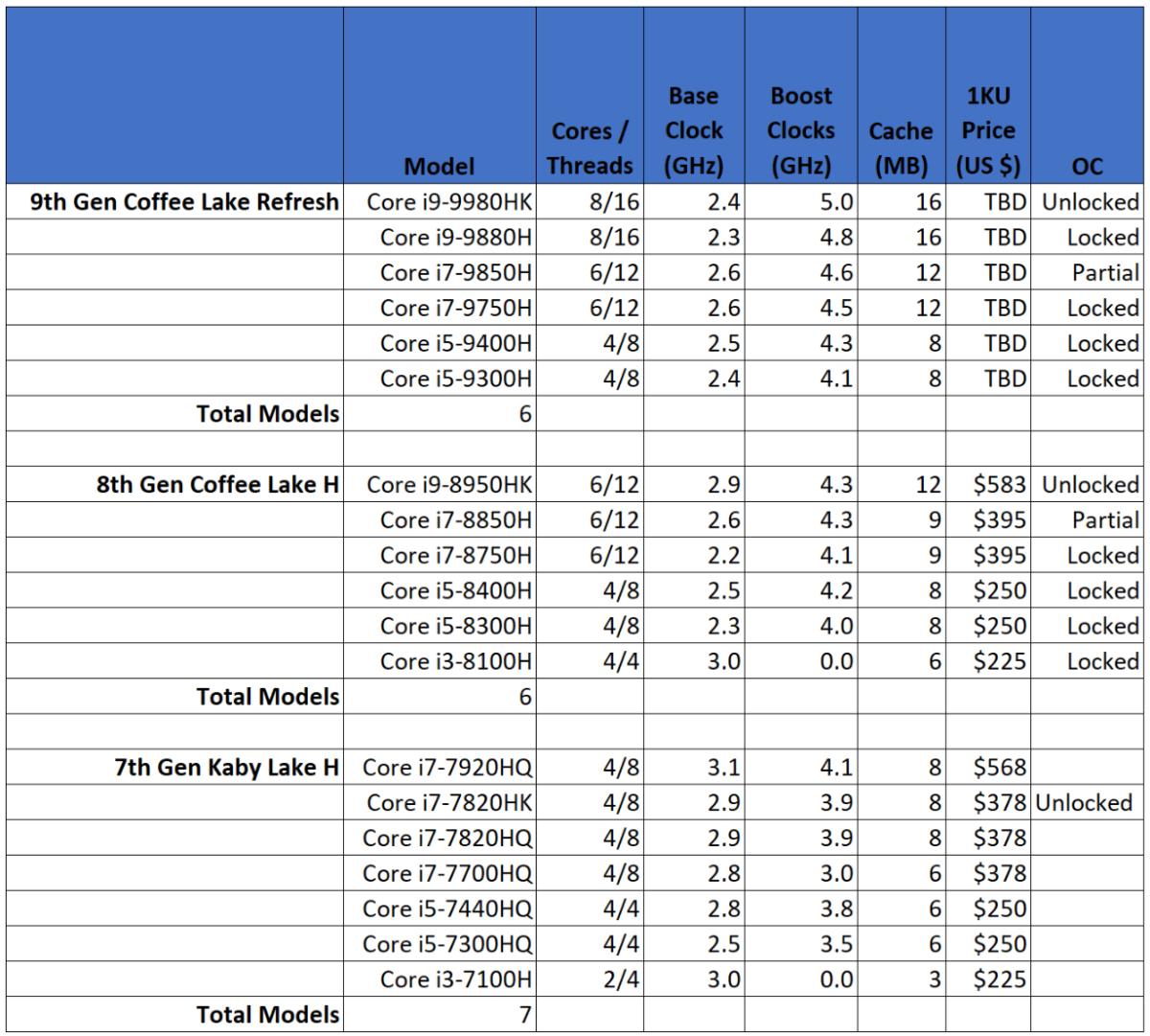
In this assignment, it has been recognized in four sections, which are introduction, content conclusion and references, each section would go in to details. First of all, in first question we would talk about some several generations of computer central processing unit (CPU), which included the stage of design and development of early CPU as well. During this section, we will make some comparison with the latest CPU and how much faster is the design and development of the latest CPU as opposed to the beginning of the CPU inventions. After that, during the secondary question in this assignment, we would create a diagram and discuss about the bus system. In this part, we should explain more detail about the bus system in term of interconnection, transmission and architecture as well.
As a conclusion, this assignment is about the function and structure of computer. The purpose of this assignment is to present as clearly and completely as possible, the characteristics and nature of modern-day computer system. Although most of the resources of this assignment are taken from internet and reference book, the objective is to present the material in a fashion that keeps new material in a clear context to those readers.
2.0 Definition of question 1
The meaning of computer architecture can be properly defined as a specification detailing that how a set of the hardware and software technologies standards interacting to form the platform or computer system. It is refers to how compatible with a computer system technologies and its design. Likewise, computer architecture also could refer to those attribute within the system, and those attribute have a direct impact on the logical execution of a program. For example, architecture attribute have include a lot of instruction set, those are the number of bits inside the program were used to represent a various data type, and the data type can be a numbers or characters.
Characteristics Of 4th And 5th Generation Computers
Besides that, I/O mechanisms and some techniques for the addressing memory also have been included within the architecture attribute. In addition, there have three type of computer architecture in our daily use, which is system design, instruction set architecture (ISA) and computer organization (known as mircoarchitecture). In short, computer architecture mostly likes to determine what the user, system or technology were needs and create some logical design and standard based on those requirement.
(Techopedia.com, 2012-2013)
3.0 The brief history of computer
The history of computer development was often referring to several different generations of computing devices. Each generation of computer is characterized by its technological development. Those purposes are wanted to increate smaller, cheaper, efficient, powerful and reliable devices.
3.1First Generation (1940-1956) Vacuum Tubes
For the first generation computer, its circuitry and magnetic drums of memory almost are making by vacuum tubes. It often larger and should have a rooms size to place it. It is very expensive to operate, since this kind of computers are enormous and should use a great deal of electricity to make it work. Besides that, it also would generate a lot of heat, so that is the most common cause to become malfunction.
The first generation computers were relied on the lowest-level programming language or machine language to perform an operation system, but it just only can solve the problem at a time. By using an input, it was based on the punched cards or paper tape, and the output would be displayed on printouts. The ENIAC and UNIVAC computers are the great examples of first-generation computing devices. The UNIVAC was the first commercial computer that delivered to a business client, which is the U.S. Census Bureau in 1951.
3.2 Second Generation (1956-1963) Transistors
While completely develop a second generation computing devices, the transistors had been developed and replaced vacuum tubes. In 1947, the transistor was already invented, but it is not widespread to use until 1950s. Though this transistor was far superior to vacuum tube, it became more reliable than their first generation predecessors, and allows computer to increasingly smaller, cheaper, faster, and more energy efficient. In fact, although the problem about generated a great deal of heat are haven’t solve yet, its improvement are still biggest than vacuum tube. Because of this reason, its input and output must still reliable on punched card and printout.
In addition, the cryptic binary machine language of second generation computer was evolving a change to languages, symbolic or assembly, which could allow programmer to specify a proper instruction in word form. Moreover, the high-level programming language had also being developed at the same time, such as the early version of FORTRAN and COBOL.
During this invention, the technology of magnetic drum had been changed to magnetic core, which means the first computer can store their instruction to their memory. So there have many atomic energy industry in this generation would started to use this type of computer to operate their system.
3.3 Third Generation (1964-1971) Integrated Circuits
For the third generation computer, the development of integrated circuit was began the hallmark. In this generation, its transistor was evolved to become miniaturized, and it could place on the silicon chips, which is called semiconductor. Therefore, it has a decisive prerequisite to increase the efficiency and speed of the computer. Besides that, it was also instead of printouts and punched cards. The user interact with the third generation computer was through the monitors, keyboard and interface with an operating system, which would allow any device to run many kind of application at a same time, and its application should run with the central program that had been monitored within the memory. Lastly, it was increasingly smaller and cheaper than before generation.
3.4 Fourth Generation (1971-Present) Microprocessors
The microprocessor was the fourth generation of the computer, it have a thousand of integrated circuits were built onto the single silicon chip. Different with the first generation, the shape of this computer now could fit into the palm of the hand as well.
For example in 1971, the Intel 4004 chip has been developed, it was located the entire component within the computer, which is from the central processing unit and memory until to the input/output controls that onto the single chip. After that, the IBM was introduced its first computer that suggest for the home user in 1981, and in 1984 Apple company introduced Macintosh. Besides that, during this generation, as a small computer to become more powerful and efficiently, Microprocessors are not only could be used in realm of desktop computer, many products in our daily use was begin to use microprocessor, for example like handheld devices, though the development of GUI, it could be easily link together and form a network, and it was led to the development of the internet.
3.5 Fifth Generation (Present and Beyond) Artificial Intelligence
For the concept of fifth generation computing devices, there are almost based on the artificial intelligence. Although this is still in development, there have some application like voice recognition was being to use. In addition, based on this development, the usage of parallel processing and superconductor was helping to make artificial intelligence to become more reality. There have some technologies were most radically change the face of computer, which is molecular, quantum computation and nanotechnology. Normally, the goal of fifth generation computing is to develop some device that could properly respond to the natural language input or become more capable of self-organization and learning.
4.0 The comparison of computer generation
Depended on this assignment, as we can see there have a very big change during those evolutions of computer generation, whether that is hardware or software components, they still have a lot of improvements to become smaller, faster and efficiently. Below diagram was obviously showing those differences between each computer generation.
COMPARISION IN GENERATIONS OF COMPUTERS
1STGENERATION
2nd GENERATION
3rdGENERATI-ON
4th GENERATION
5thGENERATION
PERIOD
1940-1956
1956-1963
1964-1971
1971-PRESENT
TODAY- FUTURE
CIRCUITRY
VACUUME TUBE
TRANSISTOR
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS (IC)
MICROPROCESSOR
(VLSI)
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGNCE
MEMORY CAPACITY
20 KB
128KB
1 MB
SEMICONDUCTOR TYPE & VERY HIGH
-
PROCESSING SPEED
300IPS
300 IPS
1 MIPS
FASTER THEN 3RDGENERATION
-
PROGRAMMING
LANGAUAGES
ASSEMBLY
LANGUAGE
HIGH LEVEL LANGAUGAE (FORTRAN , ALGOL)
C, C++
C , C++ , JAVA
-
POWER CONSUMED
HIGH
LESS COMPARE TO 1ST GEN.
LESS
LESS
-
SIZE
VERY LARGE
LESS SPACE COMPARE TO 1ST GENERATION
SMALL & CAN BE USED IN HOMES
SMALL & USED IN HOMES
-
EXAMPLES OF COMPUTERS
UNIVAC,EDVAC

IBM 1401,IBM 7094,CDC3600,D UNIVAC 1108
IBM 360 SERIES,1900 SERIES
PENTIUM SERIES , MULTIMEDIA, STIMULATION
-
5.0 Definition of question 2
For talking about the bus interconnection, the bus could properly define as a communication pathway that used to connect to two or more devices within the computer system, it also knows as a medium of sharing transmission. Whenever the multiple devices are connecting to the bus, its signal will be transmitted by any devices which their reception was available, and though receptions mostly were coming from the other devices that have been attached to the bus. In addition, if there have two devices try to transmit during at the same time period, its signal will become overlap and sometimes begin garbled. Therefore, the transmission could be successful at a time, but only did by one device.
Typically, a bus was consists a lot of multiple communication pathway and line within the computer. Actually, each line was used to transmitting signal which represented binary 1 and 0. Over the time, the sequence of binary digits could be transmitted across a single line. Likewise, the several lines of the bus could be used to transmit binary digit simultaneously. For example, the 8-bit unit of data could be transmitted over eight bus line.
In computer system, there have contains a lot of different buses that provide pathways, and these process will be provided in between the component within the various levels of computer system hierarchy. Some of the major computer components like processor, memory, and I/O are using buses to connected, and this also what we called a system bus. In short, the most general computer interconnection structure is based on the use of single or many system buses.
6.0 Bus Structure
In a system bus, it typically consists of about 50 to 100 of separate lines. Each line was assigned its particular meaning or some else function as well. Although there have many different design of a bus structure, but it would properly be classified into three categories of the function groups, which is data, address, and control lines. Below diagram was obviously showing the bus interconnection scheme.
Bus
Address lines
I/O
RAM
ROM
CPU
Control lines
Bus
Data lines
6.1 Data lines
The function of data lines which is use to provide the path for moving data among the system modules. These kinds of lines, collectively, know as data bus. The data bus may have consists of 32, 64, 128, or something even more separate line. Besides that, the numbers of the lines are begun referred as a width within the data bus. Because each of the line could only carry 1 bit at a same time, therefore the number of line would determine how many bit that could be transfer as well. The width of these data bus was a factor of key with determined that overall the system performance. For example, if there is a type of 32 bit wide and each instruction has 64 bits long of the data bus, then during each instruction cycle, the processor should access to memory module in twice.
6.2 Address lines
The function of address lines were used to designate the destination and source of the data which on the data bus. For example, if the processor would like to read a word (8, 16, 32 bits) of the data from the memory, it would put the address of its desired word onto the address lines. In short, the width of the address bus will determines the maximum possible memory capacity of the system. Moreover, typically the address lines were also using to address I/O ports. For the higher-order bits would be use to select a particular module onto the bus system, and the lower-order bits were used to select a memory location or I/O port within the module. For instance, on the 8-bit address bus, the address is 01111111 and the below might reference are located within the memory module 0 with 128word of the memory, therefore in the address 10000000 and the above refer to the devices would attached to the I/O module 1.
6.3 Control lines
The control lines mostly were used to control the entire access to and the usage of the data and the address line. Because even though the data or address lines were shared by the entire component, it should be a means to controlling them use. The control signal will transmit the both information of timing and command among the system modules. The timing signal will indicate the validity of the address and timing information. Besides that, the command signal also will specify the operation to begin to perform. Normally, there have something should be included within the control lines:
Memory write: Cause the data on the bus would be written into the address location.
Memory read: Cause the data from the address location would be place in the bus.
I/O write: Cause the data on the bus would become an output to the address I/O port.
I/O read: Cause the data from the address I/O port will be place on the bus.
Transfer ACK: To indicate which data have been accepted from or place on the bus as well.
Bus request: To indicate the module where need to gain a control of the bus.
Bus grant: To indicate the request module has already granted a control of the bus.
Interrupt request: To indicate an interrupt was pending.
Interrupt ACK: For acknowledge the pending interrupt was already recognized.
Clock: Which is use for synchronize operation.
Reset: For initializes all the modules.
7.0 Element of Bus Design
Although the variety of differences buses was implementation exist, there have some few basic parameter and element design would serve to differentiate buses. The elements of bus design which have classify to data type, method of arbitration, timing, bus width, and data transfer type.
7.1 Bus types
First of all, the bus lines could be separated to two generic types, which is dedicated and multiplexed. The differences between dedicated and multiplexed buses, dedicated bus was separate the wires for address and data and simplifies the bus protocol, which is a store operation that could put both the address and data onto the bus at the time. Besides that, the multiplexed bus almost is the same lines but used to hold either address or data at the different times. Therefore, it allow the chips could be limited the number of pins to provide a physically attached. For those given number of pins, it is usually advantageous to transfer more data.
7.2 Method of Arbitration
The purpose of arbitration in bus design issue is to provide the only one device that could put the data onto the bus at a time. Since there have many devices can sense the data, but it’s the only one can assert it. Besides that, the bus arbitration protocol was determined which the devices are getting to use the bus at any given times. Moreover, the bus arbitration also could be centralized or distributed.
Centralized arbitration
7.3 Timing
The timing could be referring to the way in which events had been coordinated onto the bus. Topically the buses are using either synchronous or asynchronous timing. Normally, in the synchronous bus, the usage of clock signal is to provide the timing for all operations. In this section, the device was presented the address on a given clock pulse, and it expects the data while during another predefined clock pulse. Besides that, in an asynchronous bus, the devices would waits for the ready signal when the data is available. Below diagram would represent a clearly definition of synchronous and asynchronous timing.
Timing of synchronous
Timing of asynchronous
7.4 Bus width
The width of this type buses is the number of line. While there have more data lines, it would more data that could be transferred simultaneously. For example, the 32 bit bus which meaning there has 32 data lines. Besides that, the more address lines, the larger and the maximum amount of memory that would be accessed. For the greater the width, there have more hardware were required to implement for the bus.
Data transfer type
Finally, there have few buses supports various, which had been classify to fetch, store, block, and wait state. At below would be showing its function and illustrated diagram.
Read- Use control line to request a fetch operation.
Store- Place an address on the address lines.
Block- the I/O controller may still communicate with the CPU or the memory with arbitrarily sized data.
Wait- When the CPU request data from RAM or an I/O device, it may not be able to get it the next clock cycle.
8.0 Conclusion
In a conclusion, we understand the computer architecture is very important for our life. Generally, the advancement of computer has really contributed much to the modern society. To making it more of a necessity are rather than complicated, computer make our life become more convenient and possible. Therefore, I could believe there still have a big improvement in advancement of computer architecture.